A subledger is a detailed record that tracks a specific subset of financial transactions within an organization. While subledger data still feeds into the general ledger, the extra layer of organization allows for more detail and reporting in specialized areas.
Some common examples of subledgers are:
- Accounts Payable (AP) - money an organization owes
- Accounts Receivable (AR) - money owed to an organization
- Payroll - wages, taxes, benefits, and more
- Cash - bank accounts, receipts, disbursements, and more
Subledger accounts can frequently live in an application outside of an ERP. This is a byproduct of subledger use case complexity. AP and AR can be so critical and confusing that some organizations may buy dedicated software to handle the process.
During the accounting close, subledger accounts still need to be reconciled. As a result, data needs to be extracted out of subledger source systems for comparison against the general ledger. The Subledger Tie Out integration allows you to gather and submit subledger data through the FloQast API to be compared against the GL balances already being brought into FloQast.
Subledger Tie Out can accept two types of subledger data: balances or transactions.
These two data objects are not dependent on each other. A user can submit a subledger balance without having backing transactions, or can submit subledger transactions in isolation from a balance. If only transactions are submitted, they will be summed and shown as the total balance with an accompanying transaction export available.
The high-level flow of submitting balances and transactions is very similar.
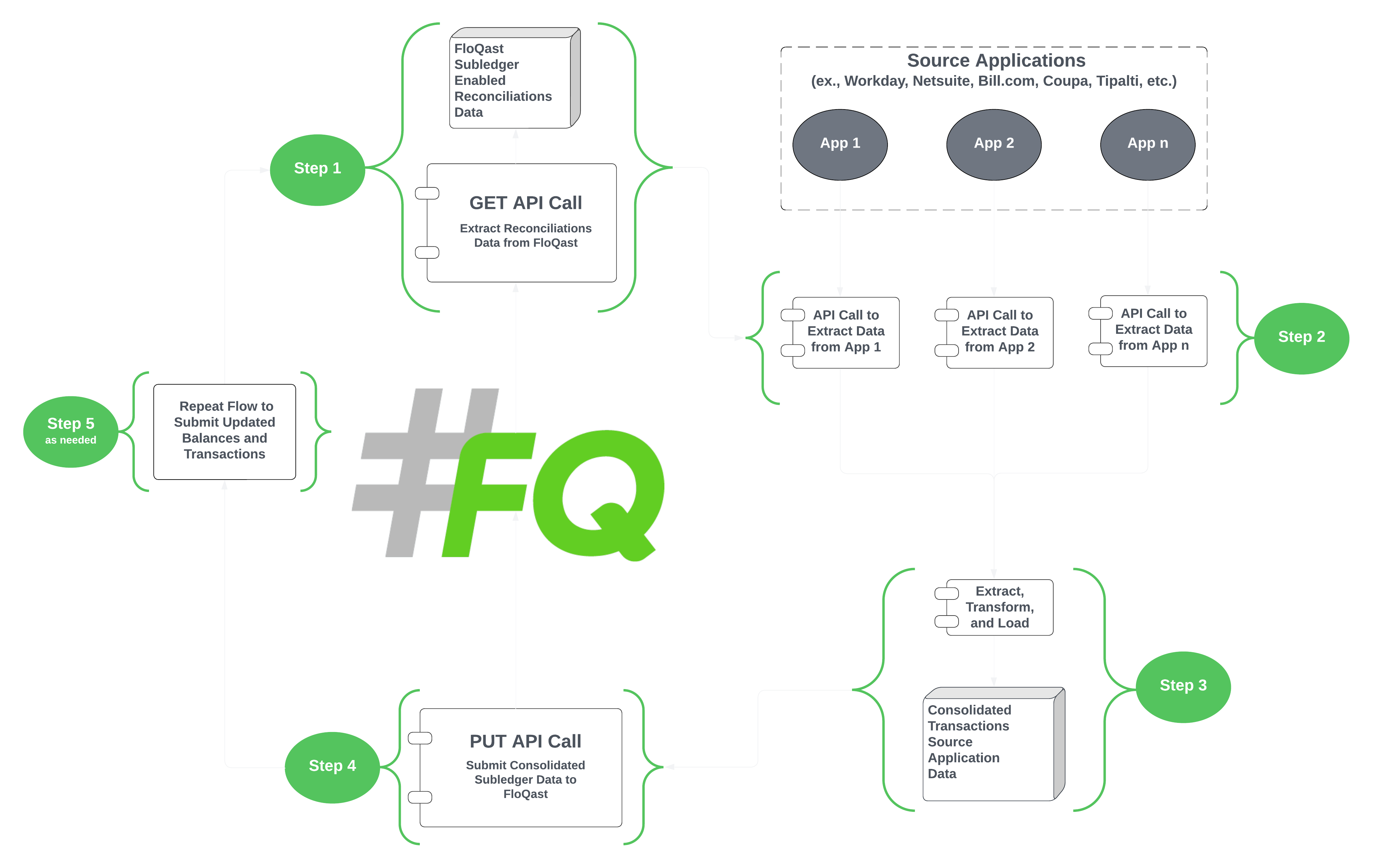
Subledger data submission starts with getting a list of FloQast Reconciliations. This provides you with the required data to map accounts to your ERP or third party systems in Step 2 and submit data in Step 3. When subledger balances or transactions are submitted to FloQast they must be sent with Reconciliation IDs.
The Reconciliation ID for a given GL account is different between each period, so you must pull new IDs each month.
For a basic overview on what makes up a Reconciliation, see the Setting Up Reconciliations API guide.
See this guide for API Key creation.
Before proceeding, you must determine which Reconciliations in FloQast are included and update their settings to accept Subledger API data. This also allows you to use the [journalSource]=SUB_LEDGER filter to limit data pulled to only these accounts.
GET Reconciliations /api/v1/reconciliations
Query parameters:
One of these is required:
filter[month]=MONTHandfilter[year]=YEARfilter[modifiedBefore]=YYYY-MM-DDfilter[modifiedSince]=YYYY-MM-DD
Recommended:
filter[journalSource]=SUB_LEDGER: limit API response to only Reconciliations of typeSUB_LEDGER
Optional:
filter[entityIds]=ENTITY_ID: limit API response to only a single entity.filter[workflowIds]=WORKFLOW_ID: limit API response to only a single workflow.filter[internalIds]=INTERNAL_ID: limit API response to specific gl internal IDs.- See documentation for more options.
Once a final list of Reconciliations and IDs has been compiled, it is time to fetch corresponding data from your subledger source systems. Due to the number of different subledger systems that exist, field names can differ significantly. A mapping exercise with the accounting team is highly recommended to ensure accounts and fields are mapped to FloQast properly.
As part of the initial GET Recs API response in Step 1, FloQast will return a gl object with several nested components that may be helpful for finding data in other systems. A particularly useful property may be gl.internalId which is often directly ties a subledger source system back to an ERP account. Depending on your ERP, FloQast will also return additional metadata such as reportingBookId and subsidiaries wherever possible.
For each target Reconciliation ID, the subledger source data will need to be mapped to FloQast's subledger JSON schema. You only need to submit balances or transactions but both are not needed.
PUT Update Subledgers
/api/v1/transactions/subledgersPUT Update Transactions
/api/v2/transactionsThe required
accountTypefield determines what kind of transaction export is available.- You only need to submit the optional fields tied to that
accountType. More can be included but they will not be visible if they are not tied to the chosenaccountType. - Review this guide for
accountTypemappings.
- You only need to submit the optional fields tied to that
When omitting the upsert value or including
upsert=false, a new API request to the samereconciliation._idwill overwrite the existing data FloQast has stored.- If data should be appended instead of overwritten, set
upsert=true.
- If data should be appended instead of overwritten, set
FloQast supports up to 2000 transactions per API request.
- If there is an account that exceeds 2000, make additional API requests with
upsert=true.
- If there is an account that exceeds 2000, make additional API requests with
Status ID: As part of subledger balance or transaction submission, FloQast API will return a statusId.
- This can be used to call GET Status to check whether or not FloQast has successfully finished processing a given job.
- It is reccomended to add this as a validation step for your integration.
To validate whether subledger data was successfully submitted in Step 3, a FloQast user will need to run the Recs Refresh process. This process can be triggered by clicking the red circled button. If a subledger balance was newly added or updated, the reconciled balance seen in blue will reflect the change.
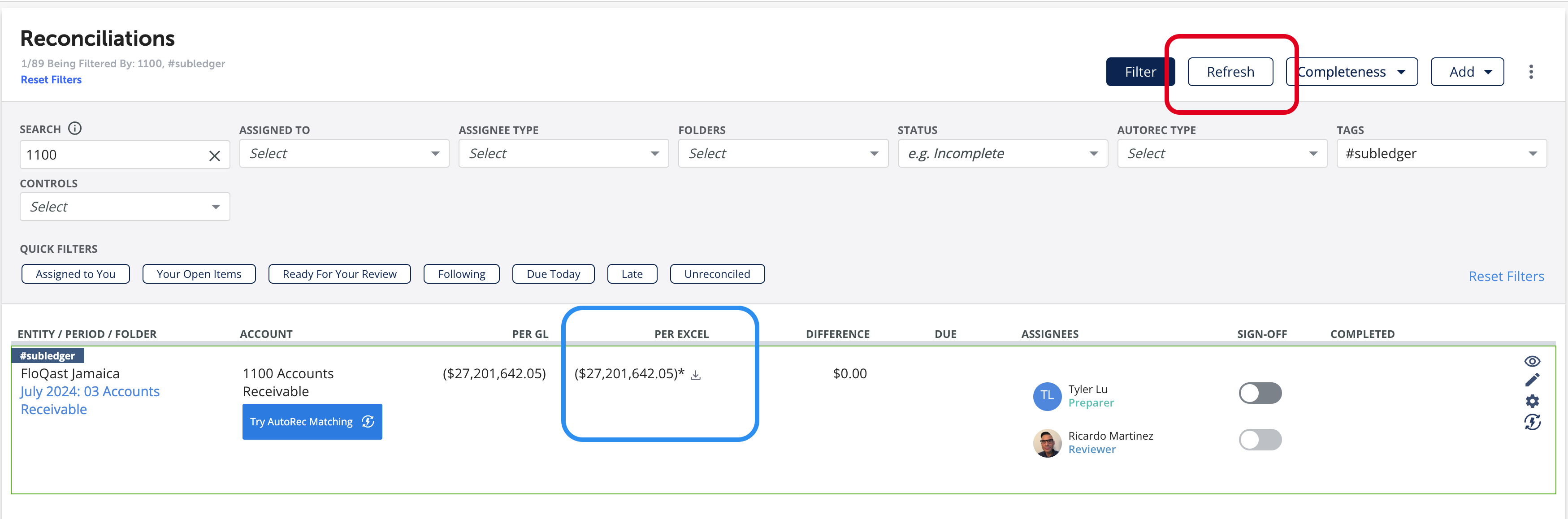
The same process applies for transactions. However, the presence of transactions on a subledger reconciliation will also render an additional download icon seen in the blue rectangle above. This download will generate an Excel file using the transactional detail sent via the API. The format of the file is determined from the accountType field.
- If you do not see data populate on refresh, confirm the Reconcilaition's settings are enabled for Subledger Tie Out.
As needed, a FloQast sandbox Entity can be created to begin sending data to those accounts before moving into production Entities. Please ask your setup lead for more information on creating Sandbox Entities.
Determine the frequency of data updates to FloQast. This is highly dependent on each organization's business requirements. More frequent is not always better, and the best source of truth is the accounting team.